
Reduced compression and oil usage due to worn piston rings/cylinder wallsĬarbon fouling occurs when the spark plug firing end does not reach the self-cleaning temperature of approximately 450☌ (842☏).
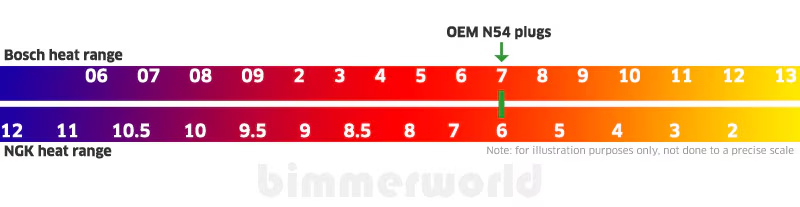

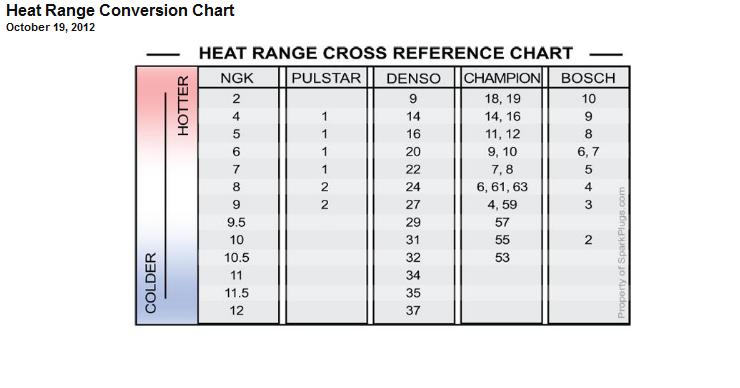
Surface area and/or length of the insulator nose.Some basic structural factors affecting the heat range of a spark plug are: Heat rating and heat flow path of NGK Spark Plugs The heat rating of each NGK spark plug is indicated by a number lower numbers indicate a hotter type, higher numbers indicate a colder type. The heat range of a spark plug is the range in which the plug works well thermally. The spark plug heat range has no relationship to the electrical energy transferred through the spark plug. This is called “thermal performance,” and is determined by the heat range selected. The spark plug firing end temperature must be kept low enough to prevent pre-ignition, but high enough to prevent fouling. A sufficient amount of voltage must be supplied by the ignition system to spark across the spark plug gap. Spark plugs must provide a path and a location for electrical energy from the ignition coil to create a spark used to ignite the air-fuel mixture. The primary function of the spark plug is to ignite the air-fuel mixture within the combustion chamber under any operating condition. The experienced tuner can use spark plugs to find the root cause of problems, determine air-fuel ratios and increase vehicle performance. The spark plug displays the condition inside the combustion chambers of the engine. Spark plugs are a “window” into the engine and can be a valuable diagnostic tool. This basic guide is designed to assist the technician, hobbyist or race technician in understanding, using and troubleshooting spark plugs. Spark plugs have been around as long as internal combustion engines have and are often a misunderstood component.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
